Sitemap
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Pages
Posts
Future Blog Post
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
Blog Post number 4
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Blog Post number 3
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Blog Post number 2
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Blog Post number 1
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
publications
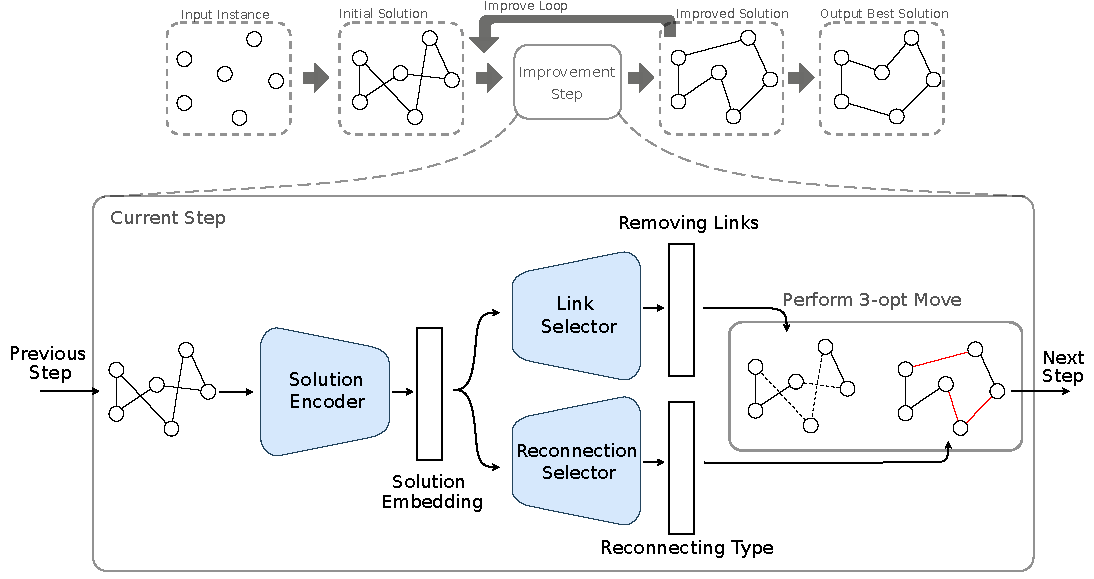
Learning 3-opt Heuristics for Traveling Salesman Problem via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Traveling salesman problem (TSP) is a classical combinatorial optimization problem. As it represents a large number of important practical problems, it has received extensive studies and a great variety of algorithms have been proposed to solve it, including exact and heuristic algorithms. The success of heuristic algorithms relies heavily on the design of powerful heuristic rules, and most of the existing heuristic rules were manually designed by experienced experts to model their insights and observations on TSP instances and solutions. Recent studies have shown an alternative promising design strategy that directly learns heuristic rules from TSP instances without any manual interference. Here, we report an iterative improvement approach (called Neural-3-OPT) that solves TSP through automatically learning effective 3-opt heuristics via deep reinforcement learning. In the proposed approach, we adopt a pointer network to select 3 links from the current tour,and a feature-wise linear modulation network to select an appropriate way to reconnect the segments after removing the selected 3 links. We demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on both real TSP instances and randomly-generated instances than, to the best of our knowledge, the existing neural network-based approaches.
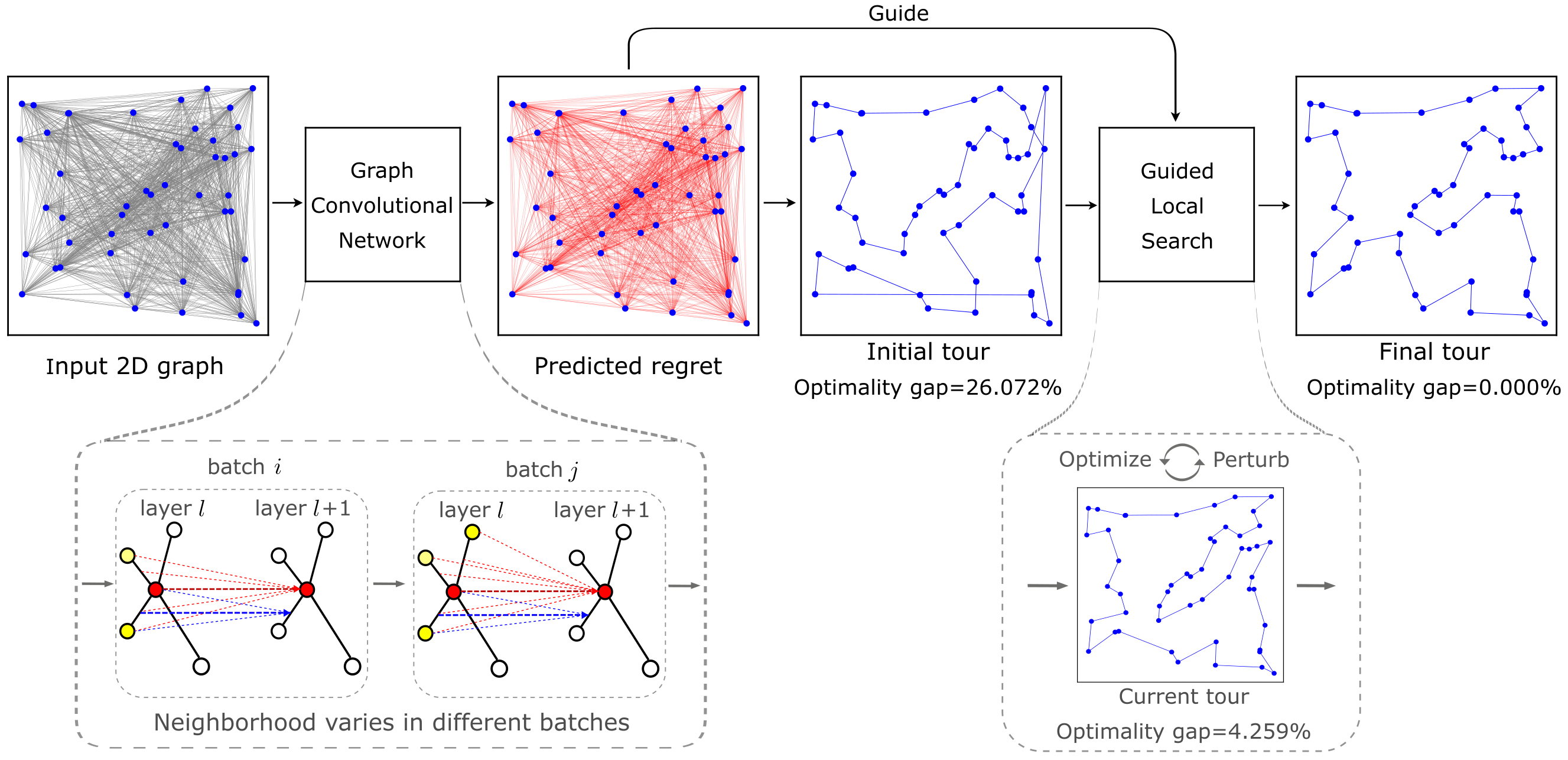
NeuralGLS: Learning to Guide Local Search with Graph Convolutional Network for the Traveling Salesman Problem
The traveling salesman problem (TSP) aims to find the shortest tour that visits each node of a given graph exactly once. TSPs have significant importance as numerous practical problems can be naturally formulated as TSPs. Various algorithms have been developed for solving TSPs, including combinatorial optimization algorithms and deep learning-based approaches. However, these algorithms often face a trade-off between providing exact solutions with long running times and delivering fast but approximate solutions. Therefore, achieving both efficiency and solution quality simultaneously remains a major challenge. In this study, we propose a data-driven algorithm called NeuralGLS to address this challenge. NeuralGLS is a hybrid algorithm that combines deep learning techniques with guided local search (GLS). It incorporates a self-adaptive graph convolutional network (GCN) that takes into account neighborhoods of varying sizes, accommodating TSP instances with different graph sizes. This GCN calculates a regret value for each edge in a given TSP instance. Subsequently, the algorithm utilizes a mixed strategy to construct an initial tour and then employs a GLS module to iteratively improve the tour guided by the acquired regret values until a high-quality tour is obtained. Experimental results on diverse benchmark datasets and real-world TSP instances demonstrate the effectiveness of NeuralGLS in generating high-quality solutions within reasonable computation time. Furthermore, when compared to several state-of-the-art algorithms, our NeuralGLS algorithm exhibits superior generalization performance on both real-world and larger-scale TSP instances. Notably, NeuralGLS also outperforms another hybrid algorithm that also incorporates GLS by reducing the mean optimality gap for real-world TSP instances from 1.318% to 0.958%, with both methods achieving results within the same computation time. This remarkable improvement in solution quality amounts to an impressive relative enhancement of 27.31%.
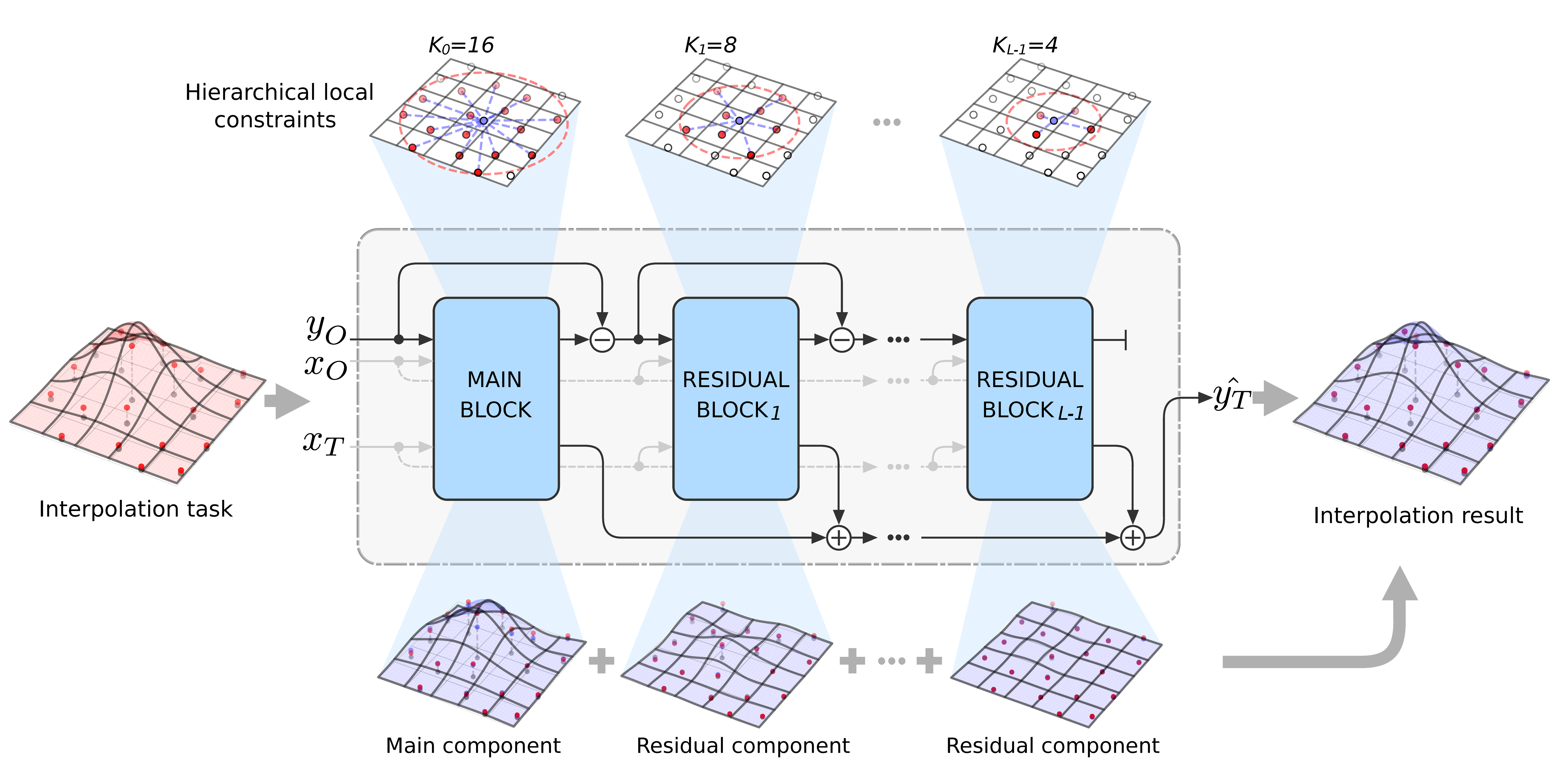
Accurate Interpolation for Scattered Data through Hierarchical Residual Refinement
Accurate interpolation algorithms are highly desired in various theoretical and engineering scenarios. Unlike the traditional numerical algorithms that have exact zero-residual constraints on observed points, the neural network-based interpolation methods exhibit non-zero residuals at these points. These residuals, which provide observations of an underlying residual function, can guide predicting interpolation functions, but have not been exploited by the existing approaches. To fill this gap, we propose Hierarchical INTerpolation Network (HINT), which utilizes the residuals on observed points to guide target function estimation in a hierarchical fashion. HINT consists of several sequentially arranged lightweight interpolation blocks. The first interpolation block estimates the main component of the target function, while subsequent blocks predict the residual components using observed points residuals of the preceding blocks. The main component and residual components are accumulated to form the final interpolation results. Furthermore, under the assumption that finer residual prediction requires a more focused attention range on observed points, we utilize hierarchical local constraints in correlation modeling between observed and target points. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HINT outperforms existing interpolation algorithms significantly in terms of interpolation accuracy across a wide variety of datasets, which underscores its potential for practical scenarios.
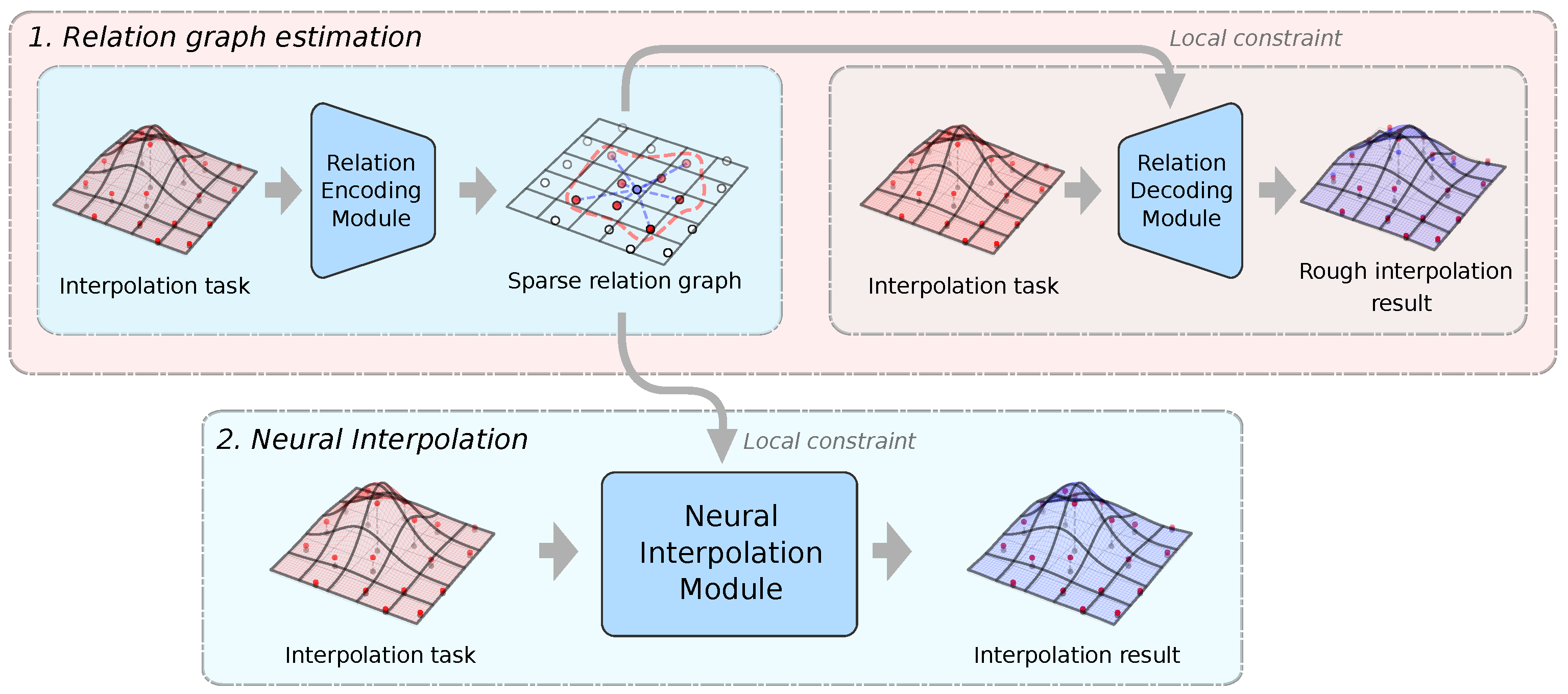
Accurate Interpolation of Scattered Data via Learning Relation Graph
Interpolation of scattered data is crucial across various domains, and neural networks have proved effective in developing accurate interpolators. While these neural network-based approaches excel in capturing data distributions, their failure to leverage inherent locality in computations can lead to overly dense correlation modeling. This might result in capturing spurious correlations and thereby affecting accuracy. To address these shortcomings, we propose a relation-aware interpolation framework named REIN. REIN uses a relational inference module to efficiently identify neighboring observed data points for each interpolation location, and integrate the relation graph as constraints into a neural interpolator. Experimental results on both synthetic and real-world datasets show that REIN outperforms the existing interpolation methods, even those employing heuristic local constraints. The analysis also suggests that compared with the widely-used heuristic local constraints, the learned local relation graphs exhibit improved adaptability and interpretability.
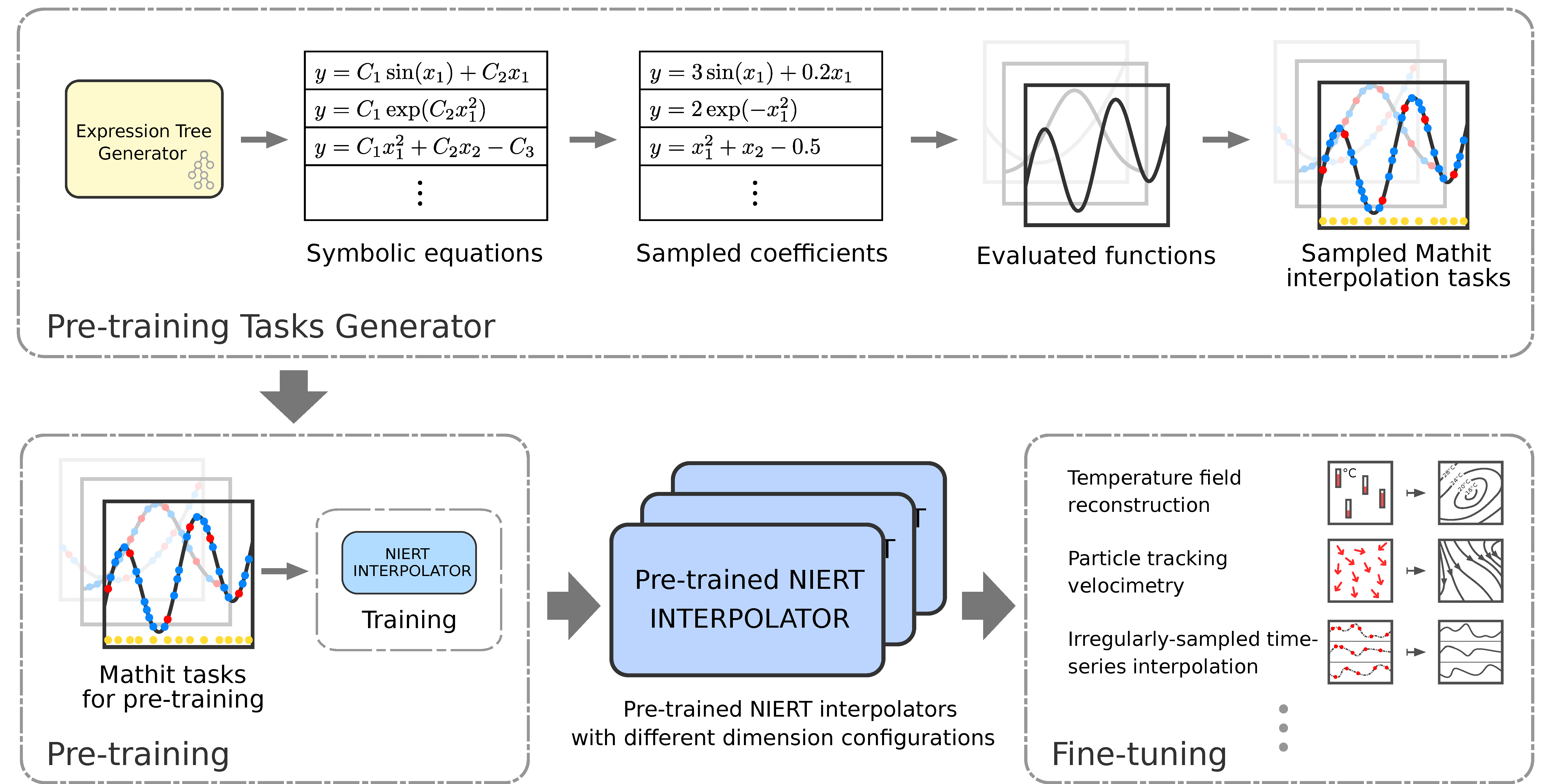
NIERT: Accurate Numerical Interpolation through Unifying Scattered Data Representations using Transformer Encoder
Interpolation for scattered data is a classical problem in numerical analysis, with a long history of theoretical and practical contributions. Recent advances have utilized deep neural networks to construct interpolators, exhibiting excellent and generalizable performance. However, they still fall short in two aspects: 1) inadequate representation learning, resulting from separate embeddings of observed and target points in popular encoder-decoder frameworks and 2) limited generalization power, caused by overlooking prior interpolation knowledge shared across different domains. To overcome these limitations, we present a Numerical Interpolation approach using Encoder Representation of Transformers (called NIERT). On one hand, NIERT utilizes an encoder-only framework rather than the encoder-decoder structure. This way, NIERT can embed observed and target points into a unified encoder representation space, thus effectively exploiting the correlations among them and obtaining more precise representations. On the other hand, we propose to pre-train NIERT on large-scale synthetic mathematical functions to acquire prior interpolation knowledge, and transfer it to multiple interpolation domains with consistent performance gain. On both synthetic and real-world datasets, NIERT outperforms the existing approaches by a large margin, i.e., 4.3~14.3x lower MAE on TFRD subsets, and 1.7/1.8/8.7x lower MSE on Mathit/PhysioNet/PTV datasets. The source code of NIERT is available at https://github.com/DingShizhe/NIERT.